Wilson's disease
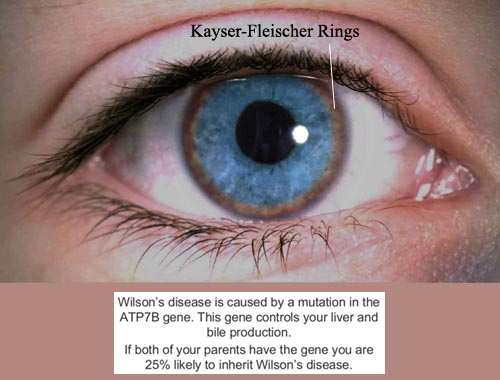
This is the rare autosomal recessive disease characterized by the deposition of copper in the brain, liver, cornea and other organs; clinical features include liver cirrhosis, liver failure, splenomegaly, tremor, bradykinesia, dysarthria, chorea, muscle rigidity, Kayser-Fleischer rings (pigmented corneal lesions), ataxia and intellectual deterioration; hepatic dysfunction may precede neurologic dysfunction by several years. The disorder caused by a defect in an enzyme involved in the biliary excretion of excess copper. Affects up to 1 in 40,000 people. Diagnosis often missed; should be considered in patients aged 10 to 40 years with hepatitis, cirrhosis, hepatic decompensation, and symptoms suggestive of movement or psychiatric disorders. Screening and diagnostic tests: 24-hour urine copper measurement, ophthalmologic slit-lamp examination for Kayser-Fleischer (KF) rings, blood ceruloplasmin levels, and liver biopsy with measurement of quantitative copper. Unlike many genetic disorders, it is treatable. Hepatic presentations are treated with a combination of trientine and zinc (liver transplantation if liver failure severe). Neurologic presentations are treated with zinc. Maintenance and presymptomatic therapy: zinc. If zinc-intolerant, trientine next best choice for maintenance.