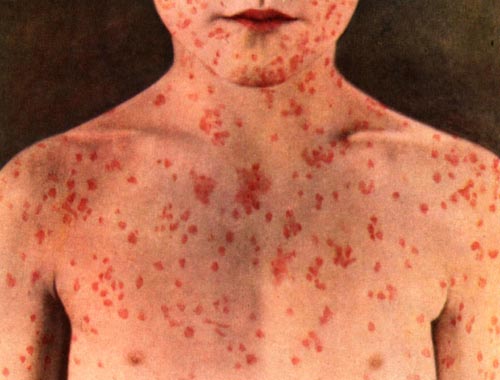
Measles (Rubeola)
Measles is one of the most contagious infectious diseases, with at least a 90% secondary infection rate in susceptible domestic contacts. It can affect people of all ages, despite being considered primarily a childhood illness. Measles is marked by prodromal fever, cough, coryza, conjunctivitis, and pathognomonic enanthem (ie, Koplik spots), followed by an erythematous maculopapular rash on the third to seventh day. Infection confers life-long immunity. Preventable by immunization but high levels of coverage are required to prevent outbreaks of disease from occurring. Complications of measles are more common in immunocompromised and poorly nourished individuals and include pneumonia, laryngotracheitis, otitis media, and encephalitis. No specific treatment for measles is available except for supportive care.