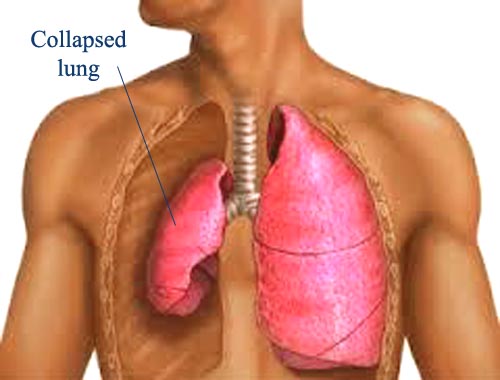
Atelectasis (Pulmonary collapse)
Atelectasis is defined as the collapse or closure of the lung resulting in reduced or absent gas exchange. It may affect part or all of one lung. It is a condition where the alveoli are deflated, as distinct from pulmonary consolidation. It is a very common finding in chest x-rays and other radiological studies. It may be caused by normal exhalation or by several medical conditions. Although frequently described as a collapse of lung tissue, atelectasis is not synonymous with a pneumothorax, which is a more specific condition that features atelectasis. Acute atelectasis may occur as a post-operative complication or as a result of surfactant deficiency. In premature neonates, this leads to infant respiratory distress syndrome. Symptoms: cough, but not prominent; chest pain; breathing difficulty; low oxygen saturation; pleural effusion (transudate type); cyanosis (late sign); increased heart rate; low-grade fever; It is a common misconception (especially among surgeons) that atelectasis causes fever. A study of 100 post-op patients followed with serial chest X-rays and temperature measurements showed that the incidence of fever decreased as the incidence of atelectasis increased.