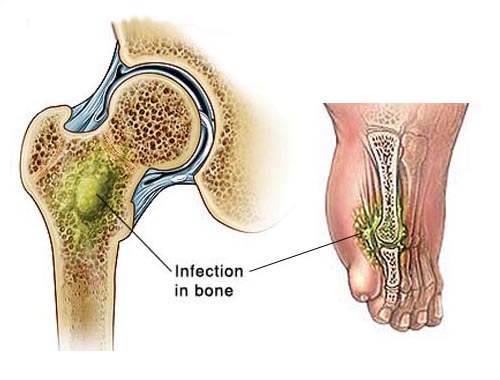
Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis is an acute or chronic inflammatory process of the bone and its structures secondary to infection with pyogenic organisms. Hematogenous osteomyelitis usually presents with a slow insidious progression of symptoms. Direct osteomyelitis generally is more localized, with prominent signs and symptoms. X-Ray still provides the best screening for acute and chronic osteomyelitis. The decision to use oral or parenteral antibiotics should be based on microorganism sensitivity results, patient compliance, infectious disease consultation, and the surgeon's experience. MRI, bone scintigraphy, and CT may be used to determine diagnosis and treatment decisions. A suppressive antibiotic regimen should be culture-directed. Staphylococcus aureus is the pathogen most commonly isolated in cultures. Operative treatment includes debridement, obliteration of dead space, restoration of blood supply, adequate soft tissue coverage, stabilization, and reconstruction.