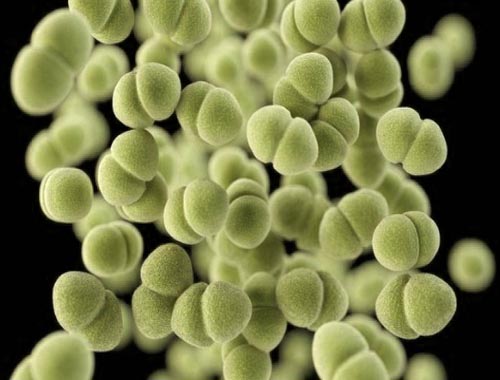
MRSA infection (Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus)
Staphylococcus aureus, often referred to simply as "staph", are bacteria commonly carried on the skin or in the nose of healthy people. Approximately 25% to 30% of people in general are colonized (when bacteria are present, but not causing an infection) in the nose with staph bacteria. When a person carries the organism-bacteria but shows no clinical signs or symptoms of infection. For Staph aureus the most common body site colonized is the nose. When there are signs (such as fever, redness, swelling, discharge, heat at a location of an infection) or symptoms (feeling feverish, chills, pain, aches, weakness, malaise - not feeling well, nausea, vomiting) of infection in addition to laboratory evidence of infection, including a positive culture. Some staph bacteria are resistant to antibiotics. MRSA is a type of staph that is resistant to a class of antibiotics related to penicillin, which includes methicillin, oxacillin, penicillin and amoxicillin. Approximately of 1% of people in general are colonized with MRSA, while people receiving certain types of healthcare, such as those receiving dialysis or living in nursing homes, are at increased risk of being colonized with MRSA.