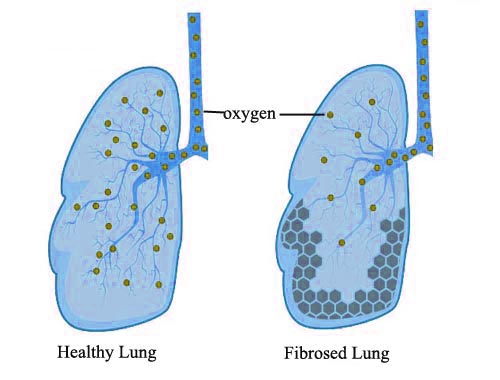
Pulmonary Fibrosis
Pulmonary fibrosis occurs when lung tissue becomes damaged and scarred. This thickened, stiff tissue makes it more difficult for lungs to work properly. As pulmonary fibrosis worsens, lungs become progressively more short of breath. The scarring associated with pulmonary fibrosis can be caused by a multitude of factors. But in most cases, doctors cannot pinpoint what's causing the problem. When a cause can't be found, the condition is termed idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. The lung damage caused by pulmonary fibrosis cannot be repaired, but medications and therapies can sometimes help ease symptoms and improve quality of life. For some people, a lung transplant might be appropriate. A rare form of fibrotic lung disease with no known etiology that progresses over the course of several years and is characterized by scar tissue formation within the lungs, dyspnea, and a significantly shortened lifespan after diagnosis. The diagnosis can be made on clinical grounds when an appropriate history of progressive symptoms (typically dyspnea and cough) is accompanied by characteristic radiographic findings and restrictive pulmonary physiology, and in the absence of findings that suggest an alternative diagnosis. Although etiology is unknown, cigarette smoking and certain environmental exposures have been implicated in the development of the disease. To date, no treatments have been shown to be effective in preventing or reversing the course of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. As a result, the most recent guidelines recommend against the use of pharmacologic therapy in most patients, although some therapies are available for consideration in a minority of patients. Important supportive measures include smoking cessation, pulmonary rehabilitation, and supplemental oxygen when appropriate. Some patients may be eligible for lung transplantation.