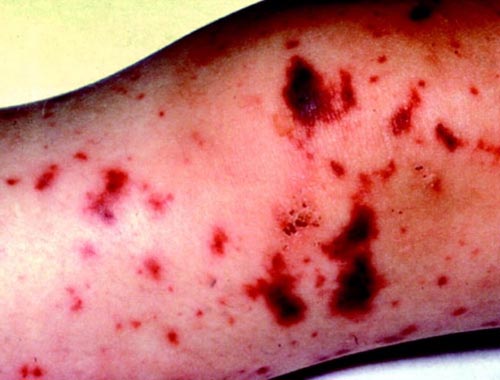
Sepsis, Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS)
Sepsis is a clinical term used to describe symptomatic bacteremia, with or without organ dysfunction. Currently, sepsis is commonly defined as the presence of infection in conjunction with the systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), with severe sepsis understood as sepsis complicated by organ dysfunction and septic shock understood as sepsis-induced acute circulatory failure characterized by persistent arterial hypotension despite adequate volume resuscitation and not explained by other causes. Sepsis can progress rapidly to multiorgan failure and shock, and is often fatal. Survival is dependent on a high index of suspicion of sepsis, early recognition, and immediate intervention. Patients with any evidence of organ dysfunction require immediate hospital assessment. Empiric broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy (based on the most probable pathogens) should be administered as soon as possible, and always within the first hour following recognition. Culture of all wounds or potentially infected body fluids should be performed, as indicated by symptoms, before initiation of antimicrobial treatment if possible. Any source of infection should be controlled as a matter of urgency, preferably within 6 hours following recognition. Evidence of hypoperfusion or shock should be sought and treated with immediate intravenous fluid challenges, if present.