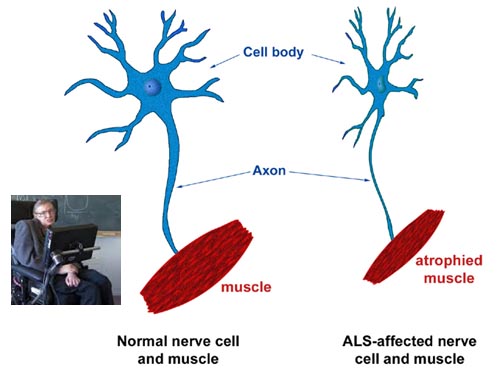
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), is a serious neurological disease that causes muscle weakness, disability and eventually death. ALS is often called Lou Gehrig's disease, after the famous baseball player who was diagnosed with it in 1939. In the USA, ALS and motor neuron disease (MND) are sometimes used interchangeably. Worldwide, ALS occurs in 1 to 3 people per 100,000. In the vast majority of cases, 90 to 95 percent, doctors don't yet know why ALS occurs. About 5 to 10 percent of ALS cases are inherited. ALS often begins with muscle twitching and weakness in an arm or leg, or with slurring of speech. Eventually, ALS affects your ability to control the muscles needed to move, speak, eat and breathe. Early signs and symptoms of ALS include: Difficulty lifting the front part of your foot and toes (footdrop); Weakness in your leg, feet or ankles; Hand weakness or clumsiness; Slurring of speech or trouble swallowing; Muscle cramps and twitching in your arms, shoulders and tongue; The disease frequently begins in your hands, feet or limbs, and then spreads to other parts of your body. As the disease advances, your muscles become progressively weaker until they're paralyzed. It eventually affects chewing, swallowing, speaking and breathing.