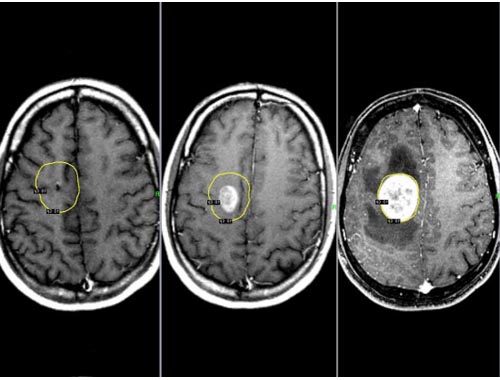
Brain Tumor, Primary CNS (Non-Hodgkin) lymphoma
A primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL), also known as microglioma and primary brain lymphoma, is a primary intracranial tumor appearing mostly in patients with severe immunosuppression (typically patients with AIDS). The central nervous system (CNS) is made up of the brain and spinal cord. A lymphoma is a cancerous tumour of the lymph cells, which are part of the body's immune system and help fight infection. Lymphomas that start in the CNS are called primary CNS lymphomas. Most of those affecting the brain are high-grade non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Some lymphomas in the head will have spread from lymphomas in other parts of the body (secondary lymphoma). It's important to know if a lymphoma in the brain is primary or secondary as they are treated differently. The most common site for a primary CNS lymphoma is the cerebrum (which is made up of the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe and temporal lobe). Sometimes more than one tumour is present. Less commonly, other parts of the CNS can be the primary site, including the lining of the brain (meninges), the eyes or the spinal cord. PCNSLs represent around 20% of all cases of lymphomas in HIV infections (other types are Burkitt's lymphomas and immunoblastic lymphomas). Primary CNS lymphoma is highly associated with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection (> 90%) in immunodeficient patients (such as those with AIDS and those iatrogenically immunosuppressed), and does not have a predilection for any particular age group. Mean CD4+ count at time of diagnosis is ~50-uL. In immunocompromised patients, prognosis is usually poor. In immunocompetent patients (that is, patients who do not have AIDS or some other immunodeficiency), there is rarely an association with EBV infection or other DNA viruses. In the immunocompetent population, PCNSLs typically appear in older patients in their 50's and 60's. Importantly, the incidence of PCNSL in the immunocompetent population has been reported to have increased more than 10-fold from 2.5 cases to 30 cases per 10 million population. The cause for the increase in incidence of this disease in the immunocompetent population is unknown.