Systemic sclerosis, Scleroderma
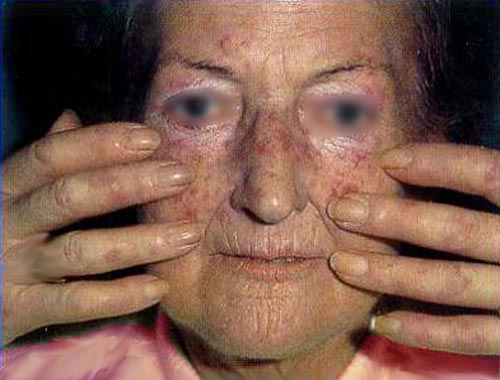
Systemic sclerosis or systemic scleroderma is a systemic autoimmune disease or systemic connective tissue disease that is a subtype of scleroderma. It is characterized by deposition of collagen in the skin and, less commonly, in the kidneys, heart, lungs & stomach. Female to male ratio is 4:1. The peak age of onset is between 30-50 years. Initial symptoms are nonspecific and include fatigue, vague musculoskeletal complaints, diffuse swelling of hands, and Raynaud phenomenon. Etiology and pathogenesis are unknown. Disease course is variable, but the condition rarely subsides spontaneously. There are two main subtypes of systemic sclerosis (SSc): limited cutaneous SSc and diffuse cutaneous SSc. The limited cutaneous form tends to have less severe internal organ involvement and a better prognosis, but these subjects still need to be followed closely for possible complications. Clinical course is determined by extent of vascular and fibrosing complications. Vascular involvement includes Raynaud phenomenon, ischemic digital ulcers, hypertensive crisis, and pulmonary arterial hypertension. Fibrosis can involve lungs, heart, and GI tract. Treatment is targeted on disease processes that are potentially reversible (e.g., active inflammation or vasoconstriction) and aims to minimize functional impairment of the patient. Scleroderma renal crisis is characterized by the onset of acute renal failure; abrupt onset of moderate-marked hypertension; a urinary sediment that is frequently normal, or reveals only mild proteinuria with few cells or casts; and a microangiopathic hemolytic anemia.