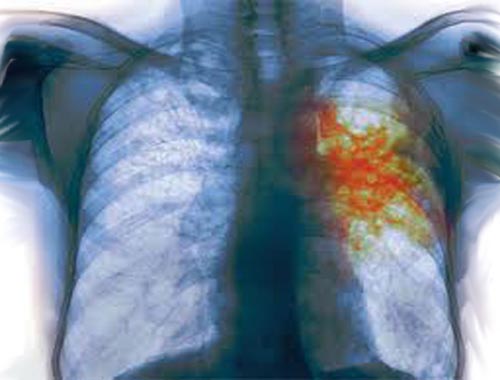
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is a potentially serious infectious disease that primarily affects your lungs. The bacteria that cause tuberculosis are spread from person to person through tiny droplets released into the air via coughs and sneezes. Tuberculosis was once rare in developed countries, but the number of TB cases began increasing in 1985. Part of the increase was caused by the emergence of HIV, the virus that causes AIDS. HIV weakens a person's immune system so it can't fight the TB germs. Many strains of tuberculosis can resist the effects of the drugs most commonly used to treat the disease. People who have active tuberculosis must take several different types of medications together for many months to eradicate the infection and prevent development of antibiotic resistance.