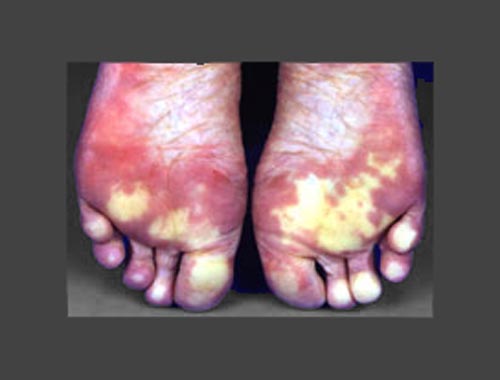
Raynaud's Phenomenon (Vascular Disease)
Raynaud's phenomenon consists of spasms of the small arteries of the fingers and sometimes the toes, brought on by exposure to cold or excitement. Certain occupational exposures bring on Raynaud's. The episodes produce temporary lack of blood supply to the area, causing the skin to appear white or bluish and cold or numb. In some cases, the symptoms of Raynaud's may be related to underlying diseases (ie, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma). Complications in secondary RP include severe digital ischemia, gangrene, digital ulcers, and infection. Pain relief and complementary therapies are important adjunctive treatments.