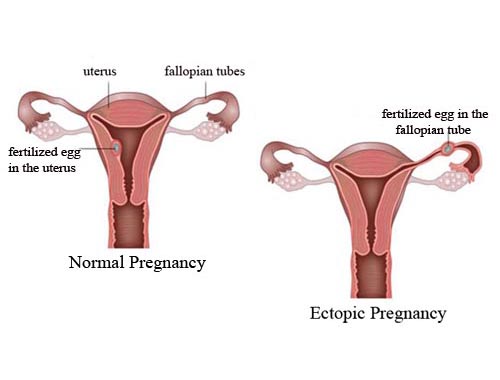
Ectopic Pregnancy, Eccysis
In a normal pregnancy, a fertilized egg travels through a fallopian tube to the uterus. The egg attaches in the uterus and starts to grow. But in an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg attaches (or implants) someplace other than the uterus, most often in the fallopian tube. (This is why it is sometimes called a tubal pregnancy.) In rare cases, the egg implants in an ovary, the cervix, or the belly. Most ectopic pregnancies can be detected using a pelvic exam, ultrasound, and blood tests.