Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP,Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura)
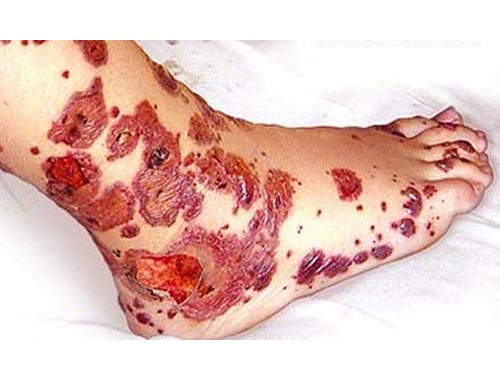
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP), also known as primary immune thrombocytopenic purpura and autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura, is defined as isolated thrombocytopenia with normal bone marrow and the absence of other causes of thrombocytopenia. The two distinct clinical syndromes manifest as an acute condition in children and a chronic condition in adults. ITP is a decrease in the number of circulating platelets in the absence of toxic exposure or a disease associated with a low platelet count. Isolated thrombocytopenia in the absence of other causes; thought to be due to an autoimmune phenomenon. Typically found in children often with a preceding viral illness and an abrupt onset, or in middle-aged women who present with thrombocytopenia with or without bleeding. Exam is usually normal. Petechiae may be present on mucosal membranes or the lower limbs. Bruising is common. Mucosal bleeding may also occur in most severe cases. Intracranial bleeding is reported in less than 1% of adults and less than 0.5% of children. CBC and smear show isolated thrombocytopenia. Bone marrow biopsy is required in patients over 60 years old to exclude myelodysplastic syndrome or lymphoproliferative disorders. Treatment is based on platelet count and bleeding symptoms. Any patient with life-threatening bleeding, regardless of platelet count, should be treated with a combination therapy of corticosteroids, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), and platelet transfusion. In children prognosis is good, with up to 80% achieving a spontaneous remission. In adults, two-thirds respond to initial treatment or splenectomy; however, 30% develop chronic disease and up to 5% to 10% of these die of hemorrhage or of treatment-related toxicity. Mortality is higher in older patients and in those unresponsive to several lines of treatment.