Mononucleosis (Mono, Epstein-Barr virus)
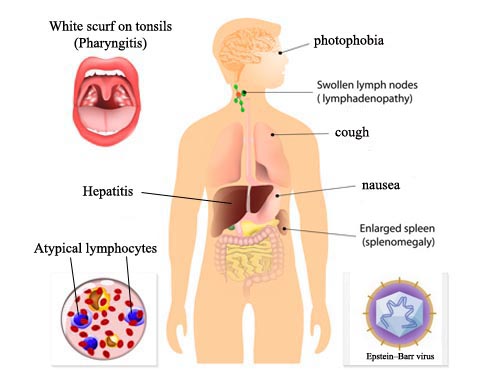
Mononucleosis is a viral infection causing fever, sore throat, and swollen lymph glands, especially in the neck. Mononucleosis, or mono, is often spread by saliva and close contact. It is known as "the kissing disease," and occurs most often in those age 15 to 17. However, the infection may develop at any age. Mono is usually linked to the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), but can also be caused by other organisms such as cytomegalovirus (CMV). Mono may begin slowly with fatigue, a general ill feeling, headache, and sore throat. The sore throat slowly gets worse. Your tonsils become swollen and develop a whitish-yellow covering. The lymph nodes in the neck are frequently swollen and painful. A pink, measles-like rash can occur and is more likely if you take the medicines ampicillin or amoxicillin for a throat infection. Characterized by fever, pharyngitis, lymphadenopathy, and atypical lymphocytosis, in older children and young adults. Often subclinical in young children. Positive heterophile antibody test and serologic test for antibodies against EBV are usually diagnostic. Rare but potentially life-threatening complications include severe upper airway obstruction, splenic rupture, fulminant hepatitis, encephalitis, severe thrombocytopenia, and hemolytic anemia. Treatment is usually symptomatic.