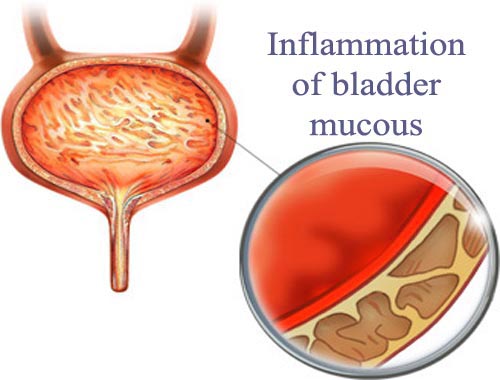
Acute Cystitis (Bladder Infection)
Cystitis is the inflammation of the bladder. Most of the time, the inflammation is caused by a bacterial infection, and it's called a urinary tract infection (UTI). A bladder infection can be painful and annoying, and it can become a serious health problem if the infection spreads to kidneys. Less commonly, cystitis may occur as a reaction to certain drugs, radiation therapy or potential irritants, such as feminine hygiene spray, spermicidal jellies or long-term use of a catheter. Cystitis may also occur as a complication of another illness. The usual treatment for bacterial cystitis is antibiotics. Treatment for other types of cystitis depends on the underlying cause. Most common etiologic organisms are Escherichia coli (80%), Staphylococcus saprophyticus (4%), Klebsiella pneumoniae (4%), and Proteus mirabilis (4%), followed by other bacteria (9%). For complicated cases of cystitis, first line is empiric therapy with a fluoroquinolone antibiotic for 7 to 14 days; treatment should be adjusted based on the results of the urine culture. Complicating characteristics include pregnancy; recent instrumentation, including catheterization or indwelling catheter; male patient; diabetes; immunosuppression; structurally or functionally abnormal urinary bladder; history of recurrent UTIs; history of infection with drug-resistant bacteria; or failed course of treatment for uncomplicated cystitis.