Fibromyalgia
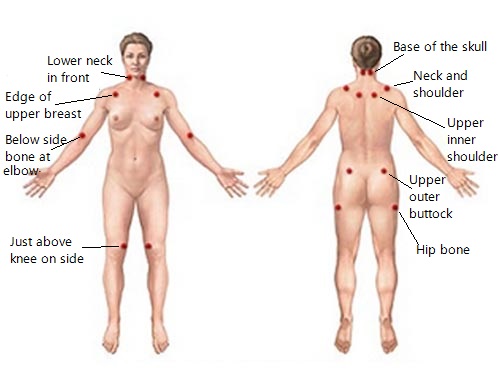
Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain syndrome diagnosed by the presence of widespread body pain (front and back, right and left, both sides of the diaphragm) for at least 3 months in addition to tenderness (digital palpation at an approximate force of 4 kg) of at least 11 out of 18 designated tender point sites as defined by the American College of Rheumatology 1990 classification criteria. The cause is not well understood, but may be related to a disordered pain perception mechanism. Classification: Primary fibromyalgia is the more common form of fibromyalgia whereby another cause for pain is not found; Secondary or concomitant fibromyalgia refers to fibromyalgia that accompanies another rheumatic disorder or follows an inciting event: Significant infection; Injury, physical; Emotional trauma; Admission to the hospital; Inciting events are not felt to be necessarily causal per se, but may trigger disordered pain perception resulting in the symptoms of fibromyalgia. Treatment and prognosis are the same as for primary fibromyalgia. Juvenile fibromyalgia is a much less common form of the condition, which occurs in children and adolescents. It carries a better prognosis than fibromyalgia in adults. An alternative classification may be useful in directing treatment options: Type I - patients with no associated processes; Type II - patients with associated rheumatic-autoimmune chronic diseases; Type III - patients with severe psychiatric disorders; Type IV - patients with simulated fibromyalgia. The common symptoms are pain, fatigue and fibro fog, but the list of possible signs and symptoms of fibromyalgia are far-reaching and body-wide; There is no radiographic or laboratory testing for fibromyalgia; the diagnosis is strictly a clinical one. However, if the patient does not meet clinical criteria for a diagnosis of fibromyalgia, then some further tests may help explain the patient's musculoskeletal pain or fatigue. Presence of chronic more than 3 months widespread body pain in the muscles and joints.