Anovulation
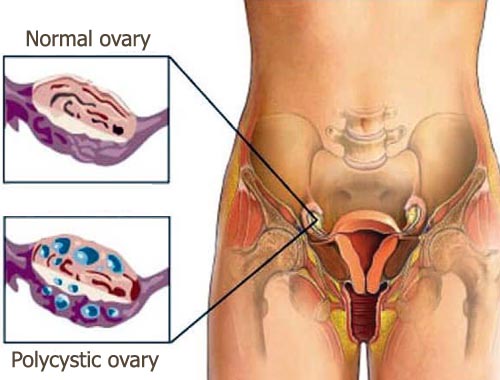
Anovulation means lack of ovulation, or absent ovulation. Ovulation, which is the release of an egg from the ovary, must happen in order to achieve pregnancy. If ovulation is irregular, but not completely absent, this is called oligovulation. Both anovulation and oligovulation are kinds of ovulatory dysfunction. Ovulatory dysfunction is a common cause of female infertility, occurring in up to 40% of infertile women. Usually, women with anovulation will have irregular periods. Or, in the worst case, they may not get their cycles at all. If your cycles are shorter than 21 days, or longer than 36 days, you may have ovulatory dysfunction. Also, if your cycles fall within the normal range of 21 to 36 days, but the length of your cycles varies widely from month to month, that may also be a sign of ovulatory dysfunction. (For example, one month your period is 22 days, the next it's 35.) It is possible to get your cycles on an almost normal schedule and not ovulate, though this isn't common. A menstrual cycle where ovulation doesn't occur is called an anovulatory cycle. Anovulation is the result of hormonal imbalances within the body. Your hormones, including estrogen and progesterone, help to trigger your body's reproductive cycle, including ovulation and menstruation. Without the proper levels of these hormones, your reproductive system can be thrown off course, preventing your ovaries from releasing an egg every month. There are a variety of different factors that can contribute to a hormone imbalance including: breastfeeding; weight gain or loss; too much exercise; extreme stress; frequent travel; eating disorders, like anorexia or bulimia.